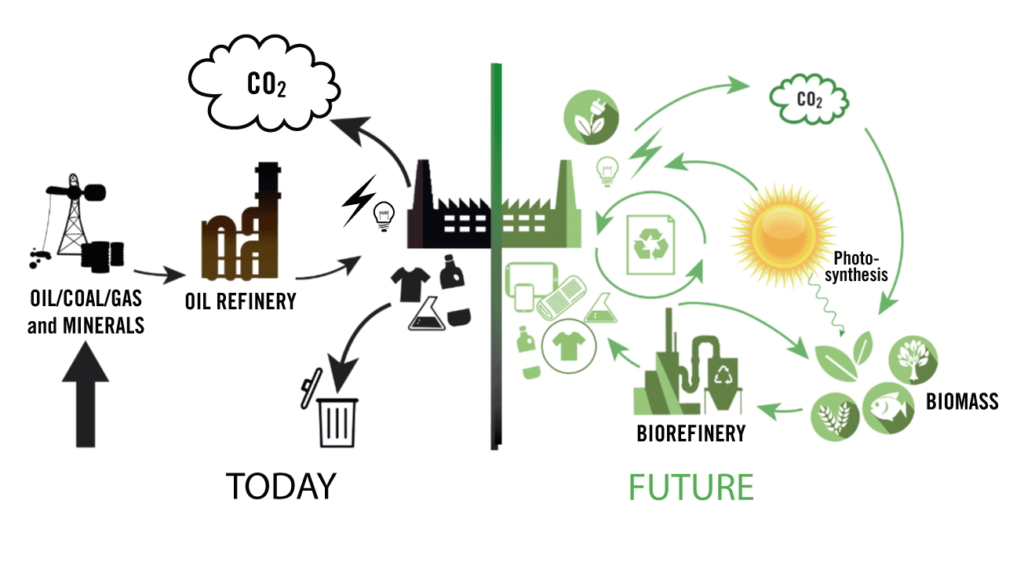
A circular economy founded on biomass instead of fossil fuels represents a significant shift in socioeconomic, agricultural, energy and technical systems. In order to make this shift happen, regions and countries need better information and the participation of the general public, including all potential stakeholders in existing and new value chains (farmers, SMEs, national and international companies, consumers, consumer associations, environmental NGOs, media, waste collectors and convertors, citizens, schools and public services etc.)
What are biobased products?
The bioeconomy is already part of our everyday lives. Many traditional products are bio-based, for example fibres from cotton, hemp or flax, or paper and other wood products. Bioethanol from sugar cane and biodiesel from oil waste are other well-known examples. Biobased materials can also be found in many other products, for example in construction materials, cosmetics, furniture or cleaning products, amongst others. Many companies are making efforts to replacing fossil feedstock with renewable biological resources in other products and processes, using innovative technologies.
Here are some examples of innovative everyday products:
Shirt by Spinnova
Spinnova produces textiles and clothing from 100 % wood-based fibers, CELLULOSE (se below). The textile is warm as a lambswool, doesn’t contain any harmful chemicals and its production is more sustainable than that of cotton. www.spinnova.fi
Each Swede consumes around 14 kilos of textiles per person per year, in stores (on-line not reported). 60% of our clothing is made of oil, but interest in for example viscose and lyocell is increasing. (Source: Swedish Environmental Protection Agency & RISE)
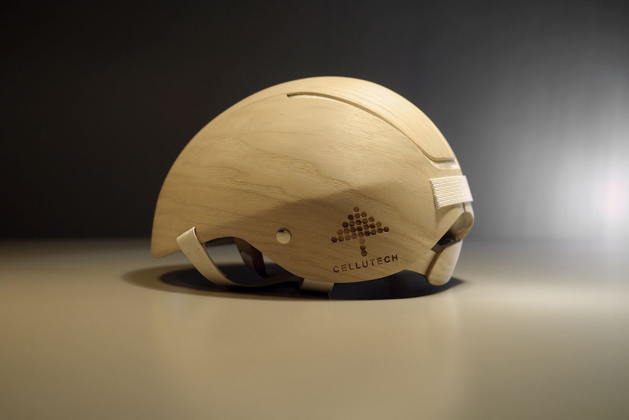


© Cellutech, Rasmus Malbert
Helmet by Cellutech
Safety helmet made out of wood veneer, a strap of durable paper and wood-based cushioning making the product. This cellulose foam is called Cellufoam™ and is made of nanocellulose.
The helmet is both renewable and biodegradable.
NANOCELLULOSE is nano-structured cellulose (se bellow). The lateral dimensions of nanocellulose range from 5 to 20 nm and the longitudinal dimension up to 2 000 nanometer. In water the Nanocellulose becomes a gel with high viscosity.


Bioplastics and paper by Vibers
Vibers products are made from miscanthus. Miscanthus or Elephant grass is a fastgrowing crop that captures CO2, four times more than European wood. Miscanthus grows on marginal land and can be processed into bioplastics and biobased materials.
There are two attributes related to bioplastics: bio-based and biodegradable. They can be one or the other or both. Read about the definitions here.
Naporo hemp insulation board
NAPORO Q-flex hemp is a flexible insulation board for walls, ceilings and roofs. The extraordinary advantages it offers are found in its excellent performance in thermal, heat and sound insulation. The raw material is hemp, a sustainable annual plant that binds four times more CO2 than european wood,

Insulating material from cellulose is a so-called high-density product. It helps to prevent unwanted air currents (convection). The Cellulose insulation high thermal capacity makes it also significantly more effective as insulation compared to for example rockwool .
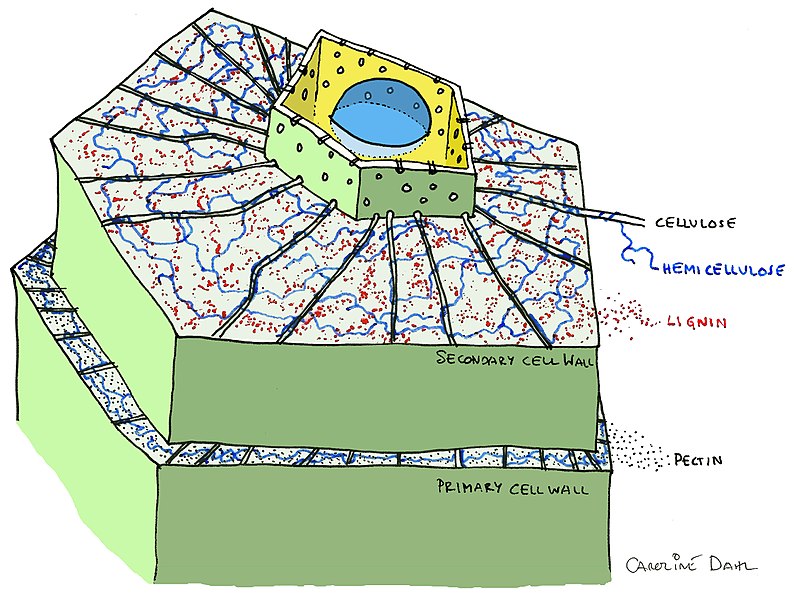
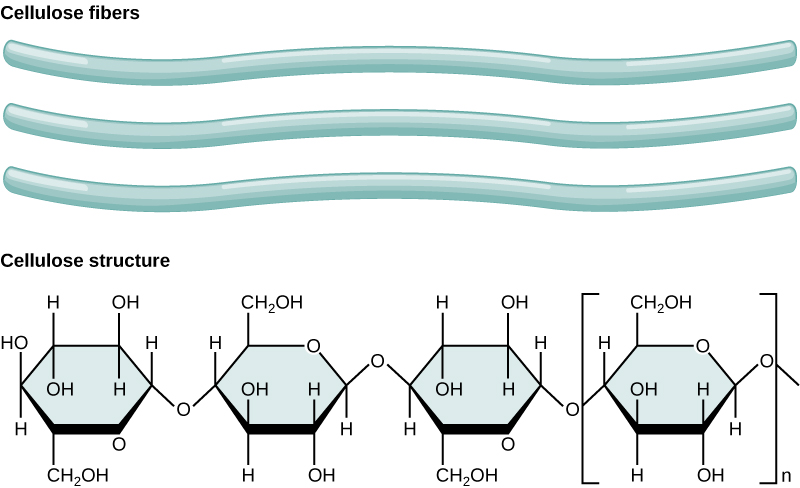
What is cellulose?